The Standardisation of ESG Reporting: ISSB will be a game changer for corporates
Key Points
• Increasing pressure from investors and other key stakeholders will drive more organisations to disclose transparent and accurate Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) information.
• With over 600 ESG frameworks and standards globally, today’s reporting landscape is both fragmented and oversaturated, leaving the business community confused and frustrated with the current system.
• The establishment of the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) will forge a path towards a global baseline of sustainability disclosures, allowing for consistent and comparable reporting standards.
Context
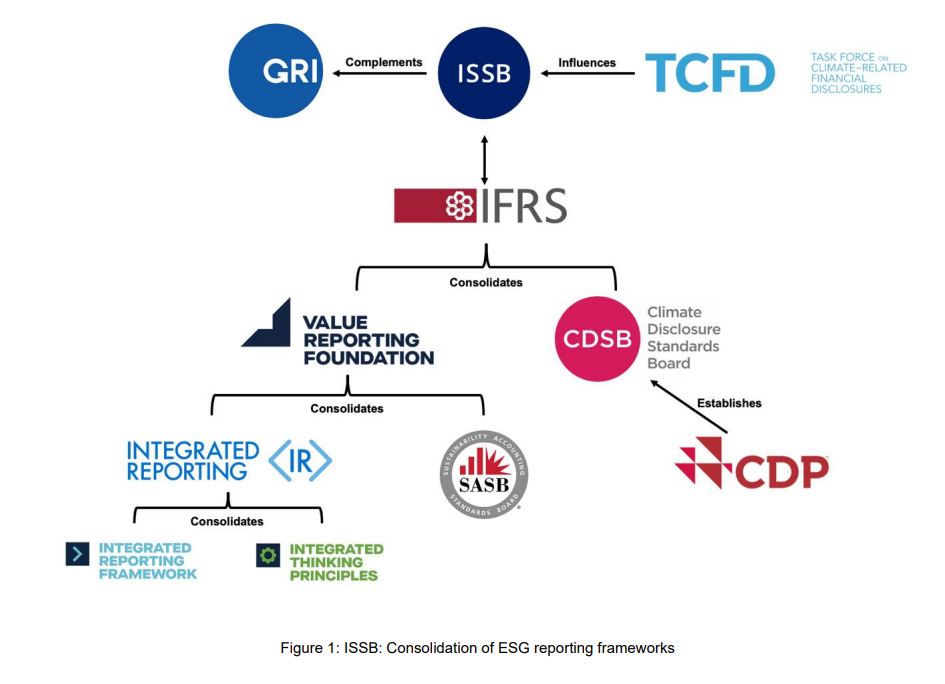
ESG reporting has become synonymous with a convoluted and overwhelming landscape stemming from erratic national legislation and a plethora of voluntary reporting frameworks, standards and ratings. Current guidance is consequently making ESG reporting more complex and opaque for organisations. However, these standards and frameworks form a critical tool with which the business community can measure, understand and communicate their exposure to a range of ESG risks and opportunities. A lack of standardised ESG data is impacting investors’ ability to make sound and informed decisions regarding companies’ ESG performances. In addition, the array of different standards allows organisations to cherry pick which issues they consider to be the most relevant, while also being heavily reliant on self-reporting. This enables business leaders to disclose only the information which portrays their firm most favourably, as opposed to providing an objective and accurate assessment. Although reporting ESG issues remains largely voluntary, mounting pressure from investors and other stakeholders has pushed disclosures from being ‘nice to have’ to essential. The legislative mechanisms necessary to operationalise ESG considerations are now coming to fruition, with clear evidence that mandatory reporting is becoming a reality. For instance, ESG reporting will be formalised through the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSDR) in the EU and the Sustainability Disclosure Requirements (SDR) in the UK; the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has also proposed new ESG disclosure rules for funds and advisors in the US. During the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26), the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation Trustees announced the creation of the ISSB as part of a push to create global ESG reporting standards.
The key objectives of the ISSB are:
- To develop standards for a global baseline of sustainability disclosures- To meet the information needs of investors
- To enable companies to provide comprehensive sustainability information to global capital markets
- To facilitate interoperability via disclosures which are jurisdiction-specific and/or aimed at broader stakeholder groups